29 Jun 2023
This article explores essential protocols (GOOSE, MMS and SV) that help ensure coordination and interoperability between IEDs and control systems. Before diving into the details, it is crucial to establish a solid understanding of several key concepts.
What is the definition of a digital substation?
A digital substation is an evolved form of a conventional electrical substation that leverages intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) in the place of analogue equipment to improve monitoring, control, and protection of power systems.
Digital substations have recently emerged as key components for efficient and reliable energy management in modern power systems. Digital substations are also capable of offering advanced features such as condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time data analysis.
What are IEDs intelligent electronic devices?
The IEDs are interconnected through robust communication networks that support fast and reliable transfer of information. Communication protocols play a crucial role in enabling seamless data exchange within the robust network.
Examples of common IEDs are advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), also called smart metres, protection relays which detect and respond to anomalies, communication gateways that facilitate the exchange of data between various devices and networks, and Phasor Management Units (PMUs) that measure and transmit synchronised phasor data. IEDs use the process bus, which replaces the analog wiring in traditional systems, to communicate with other devices on the network.
Architecture of a digital substation automation system based on IEC 61850
In the power distribution process, digital substations comprise three levels (based on IEC 61850), with each level utilizing different devices to serve specific purposes.
- The process level comprises primary power distribution equipment such as circuit breakers, busbars, and transformers.
- The bay level includes secondary equipment, such as IEDs, that interface with the primary equipment. IEDs are smart microprocessor-based protection, control, and communication devices. They collect sensor data, analyse it, and communicate with other devices on the system.
- The station level, on the other hand, consists of devices that make up the substation control system. It includes the SCADA and the Human Machine Interface (HMI). The HMI provides a simplified view of the substation equipment, enabling operators to monitor and control the devices.
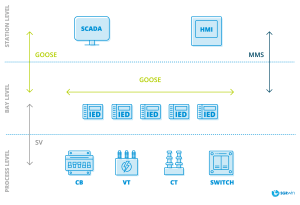
The communication networks that connect these devices can be ethernet-based, made of fibre-optic cables and UTP cables, or wireless communication systems.
Digital substations are a game-changer for power system infrastructure. They take advantage of IEDs to offer benefits such as enhanced diagnostics, reduced maintenance costs, and improved automation.
GOOSE (Generic Object-Oriented Substation Event) Protocol
The Generic Object-Oriented Substation Event (GOOSE) protocol is a communication protocol commonly used in digital substations for real-time event exchange. The protocol was designed to enable fast and reliable peer-to-peer communication while meeting the stringent power system control and automation requirements.
GOOSE utilises the publisher-subscriber model, which involves one IED acting as a publisher to transmit event messages(known as GOOSE messages) to interested IEDs within the substation network. Subscribers are referred to as the recipient IEDs.
A major advantage of GOOSE is its ability to transmit information quickly and reliably. It achieves this by utilising multicast-based communication, which allows the efficient transmission of a single GOOSE message to multiple subscribers simultaneously.
The protocol also implements a high-priority, time-critical delivery mechanism. This delivery mechanism employs synchronisation techniques to ensure accurate and synchronised event timestamps across the network.
MMS (Manufacturing Message Specification) Protocol
The Manufacturing Message Specification protocol facilitates standardised and secure information exchange between IEDs and higher-level elements such as Remote Terminal Units (RTUs). The standardised framework provided by the protocol allows the integration and interoperability of devices from various manufacturers.
MMS uses the Common Information Model (CIM) to define a common language to be used within the substation to represent system information. The model consists of a set of elements, behaviours, and attributes that facilitate a common understanding of data.
Secure communication is a key functionality offered by MMS. The protocol implements encryption algorithms, digital signatures, and other security mechanisms to ensure substation data is immune to unauthorised access or tampering.
Sampled Values (SV) Protocol
The Sampled Values (SV) protocol is a crucial protocol commonly used in digital substations to propagate high-speed, real-time analog and digital sampled values from IEDs to other devices within the substation network.
The protocol plays a crucial role in maintaining the synchronisation of data across devices in the substation by transmitting time-stamped sampled values. Synchronisation ensures the measurement samples from different devices are time-aligned and accurately represent the same point in time.
Its high data transfer rate allows quick exchange of sampled values, which is essential for capturing and responding to transient events or faults with minimal delay.
Other Protocols Used in Digital Substations
While GOOSE, MMS, and SV are integral to digital substations, several additional communication protocols are commonly employed.
- IEC 60870-5-101/104: This protocol supports reliable communication between IEDs and control centres to support substation automation.
- DNP3 (Distributed Network Protocol): DNP3 offers secure, efficient, and robust communication for SCADA systems. It provides seamless data exchange between master stations and outstations, enabling real-time monitoring, control, and data acquisition.
- ICCP (Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol): ICCP facilitates secure and reliable communication between multiple control centres. Using the protocol, these centres can exchange real-time data such as system conditions, measurements, and control commands.
Legacy Protocols
While the modern protocols mentioned above are the preferred alternatives for digital substations, legacy protocols such as the IEC 60870-5-104 (often called IEC 101), IEC 60870-5-101 (often called IEC 104), and Modbus have remained prevalent in the industry.
The protocols were developed earlier and may lack the advanced features and security mechanisms of their modern counterparts. However, many companies keep using them due to existing infrastructure, compatibility constraints, or cost considerations among other issues.
The coexistence of new and legacy protocols poses challenges that inhibit the effective integration and interoperability of digital substations. This challenge sheds light on the importance of solutions that can seamlessly handle multiple conventional and modern protocols, ensuring efficient communication and interoperability across various devices and systems.
Monitor and manage GOOSE, MMS and SV protocols with SGRwin’s D-Substation Module
GOOSE, MMS, and SV are effective protocols that form the backbone of data exchange in digital substations. These protocols ensure real-time event exchange, secure information sharing, and accurate measurement transmission.
SGRwin’s D-Substation module enables seamless communication and interoperability among relays, switchgear, control systems, and other devices within digital substations. Additionally, it ensures efficient connectivity and integration for both internal and external communication requirements in the substation environment.
Benefit from real-time event tracking, network wide visibility, and comprehensive substation monitoring. With support for MMS, GOOSE, SV, 101, 104, and many other protocols, our tool guarantees seamless integration.
We are currently in the development phase and are actively testing the D-Substation module in client environments. These comprehensive tests will ensure our solution is robust, reliable, and capable of meeting the evolving needs of digital substations.
Feel free to share your project requirements, we’ll be delighted to provide you with our assistance.
